Mohammed Al-Sulami
RIYADH: Members of the international community with open channels to Yemen’s Houthi militia must use their leverage to encourage it to sever ties with Iran and commit to the Saudi-led peace initiative, a senior Yemeni Cabinet minister has said.
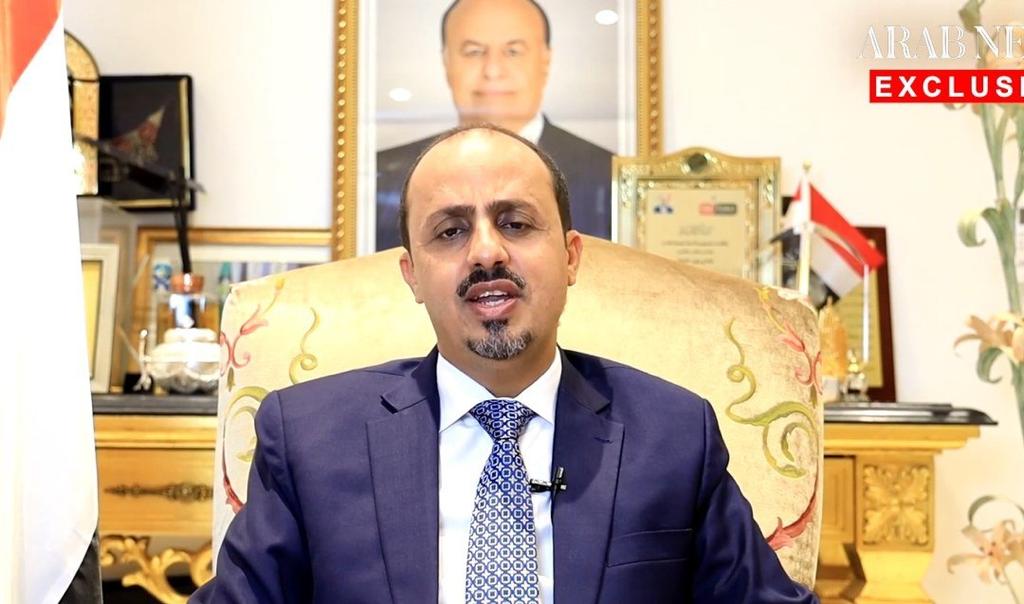
Moammar Al-Eryani, Yemen’s minister for information, culture and tourism, issued the appeal in an exclusive interview with Arab News, adding he was under no illusions about the role of Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRCG), in particular its extraterritorial Quds Force, in the Houthis’ ongoing military offensive in Marib and its attacks on civilian facilities and commercial shipping.
“Although we understand that the Houthi militia is merely a dirty tool to carry out the Iranian agenda of targeting Saudi Arabia, spreading chaos and terrorism in the region and threatening commercial ships and international shipping lanes, we call on countries that are communicating with the Houthis to play a constructive role,” Al-Eryani said.
He added these countries should pressure the militia to “drop Iranian guardianship over its political and military decisions,” to “immediately halt its military escalation in Marib,” and to “immediately and unconditionally respond to the initiative made by our brothers in Saudi Arabia.
“These countries must put pressure on the Houthis to stop their daily crimes and violations against civilians in their areas of control, which are considered war crimes and crimes against humanity,” he said.
Tehran installed Quds Force officer Hassan Irloo as its ambassador in the Yemeni capital, Sanaa, in Oct. 2020, making Iran the only nation to officially recognize and appoint formal representation to the Houthis. Irloo, a Quds Force veteran, has been sanctioned by the US Treasury for his role in the supply of advanced weaponry to the Houthis.
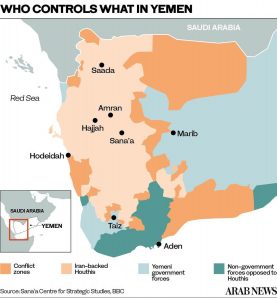
The militia, which has control of most of Yemen’s north, has been battling forces loyal to President Abd-Rabbu Mansour Hadi’s internationally recognized government with funding and weaponry provided by Iran as part of its proxy campaign across the Middle East.
The military and financial support given by Iran to the Houthis has been an open secret from long before the militia’s takeover of Sanaa in 2015. The general consensus of security analysts is that Tehran’s malign influence has fanned the flames of war, undermined numerous peace attempts and contributed to the world’s worst humanitarian crisis.
The US State Department listed the Houthis as a Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO) on Jan. 19 in one of the final acts of the Trump administration in its “maximum pressure” campaign against Iran and its proxies in the Middle East.
However, with the Biden administration reversing the FTO designation on Feb. 15 with the stated objective of easing the humanitarian situation in the country, the Houthis have ratcheted up their assaults on Yemeni government forces, and targeting of Saudi population centers and civilian infrastructure with missiles and drones.

“The decision of the US administration to delist the Houthis as a terrorist organization has disappointed Yemenis, who saw it as encouraging the militia to carry out more crimes and violations against civilians,” Al-Eryani said.
“They also saw it as giving the Houthis a free hand to launch a military offensive in Marib province, to increase the frequency of terrorist attacks on civilians and vital installations in Saudi Arabia, and to threaten the security and stability of global energy supplies, as well as international shipping lanes in the Red Sea and Bab Al-Mandab.”
Al-Eryani said the terror-delisting decision ignored the truth about the Houthis’ association with the IRGC, as well as “their extremist views, hostile slogans and criminal practices against civilians in their areas of control, which are no different from those of other terrorist groups.”
The Houthis’ disregard for civilian lives was further demonstrated on March 7 when scores of Ethiopian migrants kept in a detention camp in Sanaa were burned alive after teargas canisters and flash bangs fired by guards caused a fire.
For Al-Eryani, the only thing worse than the atrocity itself was the silence of normally outspoken rights groups and the international community.
“Unfortunately, the horrific crime for which the Houthi terrorist militia claimed responsibility, killing and injuring dozens of African migrants in a deliberate fire in one of the detention camps, has not received much attention from the international community or international human rights organizations, except for a few timid statements,” Al-Eryani said.

“This shameful and unjustified international silence regarding the crimes and violations of the Houthi militia is not limited to just this incident. Consider the thousands of crimes and violations committed by the militia in cold blood against innocent women, children and the elderly, including the attempt to target the government at Aden International Airport.”
According to diplomats, an investigation by a UN team of experts has found that the Houthis were responsible for that Dec. 30 attack, which killed at least 22 people and injured dozens more. Missiles landed just as Yemeni government officials arrived at the airport to join members of the Southern Transitional Council in a new cabinet as part of a Saudi-led reconciliation effort. The dead included government officials and three ICRC staff members.
According to Al-Eryani, since their emergence in the Saada governorate in the early 2000s, the Houthis have perpetrated all sorts of crimes against defenseless civilians, including: “Killings and kidnappings; forced disappearances; psychological and physical torture; assaults on women in secret detention centers; looting of public and private properties; bombing of opposition houses and mosques; child soldier recruitment; compulsory conscription of civilians and refugees; planting of land and sea mines, and attacks on commercial vessels and oil tankers in international sea corridors.”
Saudi Arabia has led repeated attempts to reach a comprehensive resolution between the Houthis and the Yemeni government. The latest attempt came on March 22, when it announced a wide-ranging initiative that calls for a UN-supervised nationwide ceasefire, the reopening of Sanaa airport, and new talks to end the conflict.
Al-Eryani believes it is Iran’s influence over the Houthis that has stalled progress on the plan.
“The Saudi initiative came at an important and crucial time to clearly reveal the role played by Tehran in undermining efforts to bring peace to Yemen, and the role of Irloo as the de-facto ruler in Sanaa. Irloo controls the political and military decisions of the Houthi militia,” Al-Eryani said.
Negotiations being necessarily a two-way street, Al-Eryani says the Yemeni government has already shown it is willing to make concessions. “During the rounds of consultations with the Houthis under the auspices of the UN, the government made many concessions to stop the bloodshed and end the suffering of Yemenis,” Al-Eryani said. “But the Houthis dealt with these concessions with indifference and exploited them to regroup and compensate for its human losses, and also to amass weapons smuggled from Iran such as ballistic missiles and drones for military re-escalation and in an attempt to impose its coup.”

In addition to the war and humanitarian crisis in Yemen, the international community has urgent business in the form of the FSO Safer — an abandoned oil tanker moored off Yemen’s western coast. Unless the Houthis allow urgent repairs to take place, the vessel’s payload — 48 million gallons of oil — could spill into the Red Sea, devastating the environment and coastal fishing communities.
While announcing the Kingdom’s latest peace initiative in Riyadh, Prince Faisal bin Farhan, the Saudi foreign minister, described the dilapidated ship as a “ticking time bomb” in view of its potentially destructive ecological impact.
“The Saudi foreign minister’s description is very accurate,” said Al-Eryani. “The Houthis are using the FSO Safer as a time bomb and a means to blackmail and pressure the international community for political and material gains. Unfortunately, the Houthis are not interested in the looming environmental, economic and humanitarian disaster.”
Expressing the Yemeni government’s concerns on the FSO Safer issue, Al-Eryani said: “We call on the international community, primarily the member states of the UN Security Council to put pressure on the Houthis to immediately and unconditionally implement the agreements with the UN, and to allow the technical team to assess the status of the Safer and avoid a disaster that will have serious consequences for all Red Sea countries and will affect the region and the world.”
_______
• Twitter: @md_sulami