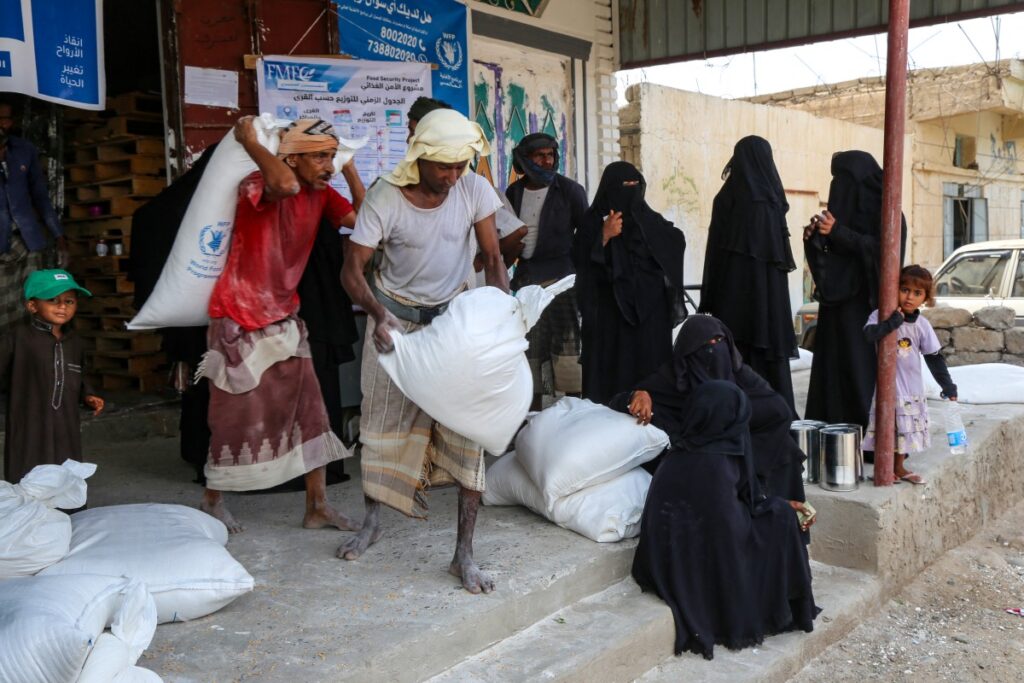
A recent policy report released jointly by the International Committee of the Red Cross, or ICRC, and the Norwegian Red Cross, sheds light on the alarming exacerbation of humanitarian needs in the region. This report, titled “Making Adaptation Work: Addressing the compounding impacts of climate change, environmental degradation, and conflict in the Near and Middle East,” sheds light on the dire situation faced by communities in the region.
The ICRC report emphasizes that climate change is not solely an environmental issue but a significant threat to human security, further exacerbating existing vulnerabilities. The report highlights the intricate connections between marginalized communities, armed conflicts, and humanitarian crises, emphasizing the urgent need to address these interconnected challenges.
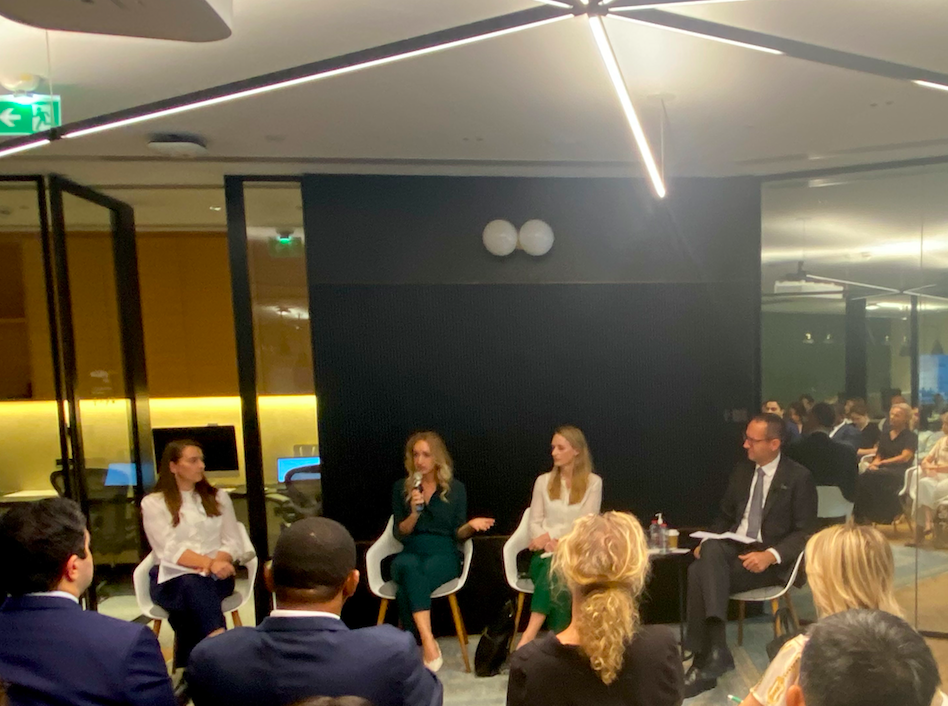
To delve into the intricate interdependencies between climate resilience, conflict-affected regions, and the imperative need for climate financing, a panel of experts convened in Dubai recently to explore this multidimensional crisis. The participants of the forum included Clare Dalton, the ICRC’s head of delegation in the UAE, Trond H.G. Rudi, charge d’affaires of the Norwegian Embassy in the UAE, and Helena de Jong, senior advisor of the UAE COP28 team.
Climate financing for conflict-affected regions
In conflict-affected countries, the challenge lies not only in combating climate change but also in navigating complex socio-political dynamics. Dalton emphasized that climate financing must be effectively channeled to countries grappling with conflict. The outcome she hopes to see from COP28 in the UAE is that “climate financing is better directed to countries experiencing conflict in ways that they can practically apply and use.” However, the current state of affairs presents obstacles, such as unreliable banking systems and numerous other factors that impede effective climate financing.
The report sheds light on the formidable barriers faced in accessing multilateral climate finance for state-led adaptation projects in conflict-affected countries. These challenges materialize as a result of stringent governance prerequisites and a certain aversion toward investing in volatile contexts.
As of January 2022, a mere 19 single-country projects in Iraq, Syria and Yemen have successfully secured funding approval, with the disbursed amount accounting for less than 0.5 percent of the global allocation of climate project funds. This stark disparity underscores the pressing need to address the limited access and utilization of climate financing in conflict-affected regions.
To overcome these obstacles, Dalton advocates for the collaboration of all sectors of society, emphasizing the necessity for concerted efforts in order to develop tangible, implementable solutions.
While the ICRC acknowledges that it operates at the periphery of climate negotiations, it recognizes the necessity of addressing climate change due to its impact on the regions it serves. Achieving this requires tangible strategies and concrete actions that go beyond mere agreement on the importance of adaptation.
“It’s not the fact that we all agree this needs to happen, but it’s the how. What are some very concrete ways that this could happen tomorrow because it’s needed then after the COP. And I think that happens in two ways because it’s not just in the form of negotiations, but it’s also in providing the space for actors to come together and look at some of these issues. So I think my second expectation is that we find a way to do that. You know, the remaining question is who can help us achieve that outcome. So yeah, money in places like Somalia, Yemen, Iraq, and any of these places that need that support,” Dalton said.
Dalton also touched on how small-scale initiatives play an important role in building community resilience amidst the challenges associated with the de-prioritization of climate action in conflict-affected settings, citing solutions such as education on sustainable agricultural practices, and the distribution of climate-resilient seed varieties to strengthen food security and build community resilience.
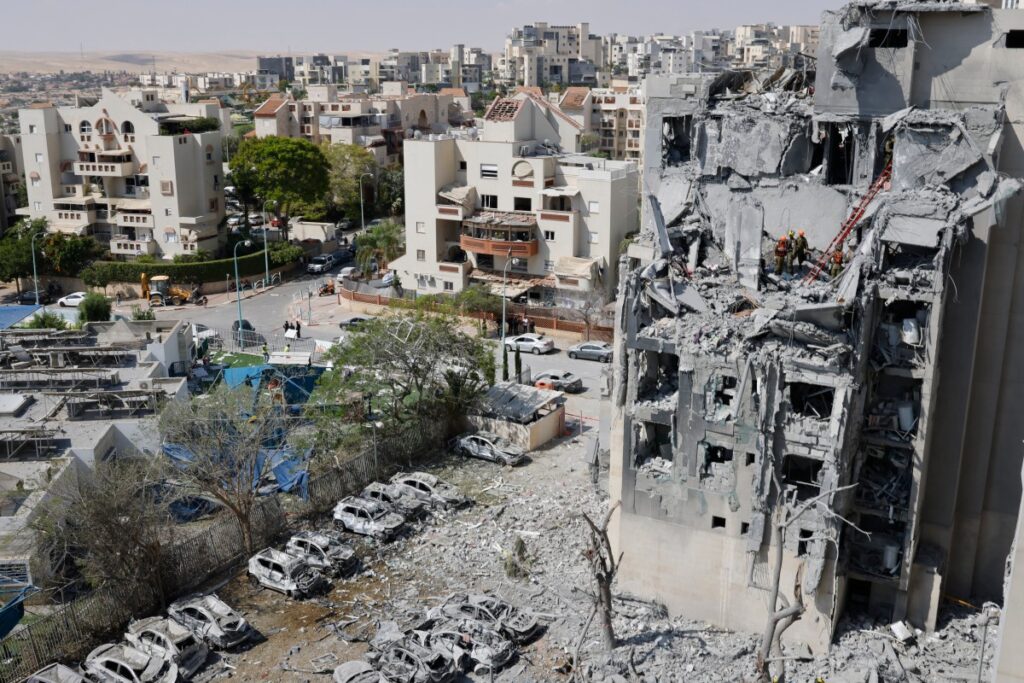
Armed conflicts exert a dual impact on the environment, both directly and indirectly, with profound consequences for human well-being. Such conflicts erode environmental governance structures and disrupt societal order, thus perpetuating the conditions conducive to environmental degradation. Consequently, the direct environmental harm caused by conflict and the subsequent degradation of ecological systems undermine the availability of natural resources, rendering communities more susceptible to the repercussions of climate change.
The report presents compelling instances that highlight how deliberate acts of environmental degradation can heighten the immediate jeopardy faced by significant population groups. A notable example is the seizure of Iraq’s Mosul Dam in 2014, which precipitated a looming risk of dam collapse. The accompanying threat to intentionally destroy the dam and flood downstream Baghdad underscores the urgent requirement for increased vigilance and accountability in safeguarding critical infrastructure systems and protecting vulnerable communities.
Dalton highlighted the imperative of engaging with the inhabitants of conflict-affected regions, acknowledging their lived experiences and incorporating their perspectives into climate resilience initiatives, stating: “We need to listen to those people about what changes they’ve seen, about what solutions they perceive might be.”
This approach recognizes the significance of local knowledge and ensures that adaptation strategies are contextually relevant and responsive to the specific challenges faced by these communities. By fostering connections between local, national, regional and global levels, a comprehensive and integrated framework can be established, incorporating diverse solutions and approaches to address the multifaceted issues arising from climate change and conflict.
“Communities need to understand how they can be part of the solution as well and what they can do in their own way not to make the situation any worse. And that’s exactly the same for humanitarians. We have that ‘do no harm’ principle. How can we respond to people’s needs but without making it any worse for them in terms of the assistance we give?” she said.
Revisiting climate-finance priorities
The report draws attention to the discrepancies between climate finance flows, vulnerability to climate change, and countries torn by conflict. De Jong, the senior advisor of the UAE COP28 team, highlighted a distressing statistic: out of the 46 countries listed as least developed, 22 are affected by conflict and fragility.
Paradoxically, these conflict-ridden nations receive the least amount of climate finance, exacerbating their vulnerability to both conflict and climate change. This predicament perpetuates a vicious cycle, hindering governments’ capacity to tackle these intertwined challenges effectively. To break this cycle, De Jong advocates for a paradigm shift in climate financing, with a renewed focus on prioritizing conflict-affected nations. She highlights the importance of engaging climate finance providers, multilateral development banks, humanitarian organizations, and peacebuilding actors in finding solutions.
“This is something that we would like to see changed. It’s not easy. This is a fairly complicated problem. But the advantage of focusing on this as a COP28 presidency is that we can talk to all these climate finance providers, so we can talk to the multilateral development banks, and we can talk to humanitarian actors and peacebuilding actors in this space to really bring all of them together to look at the solutions. Because the solutions are there. We know that there are plenty of actors that are able to work in these settings,” De Jong said.
Global pact for climate adaptation
To address this imbalance, De Jong proposes a paradigm shift in climate financing, with a renewed focus on prioritizing conflict-affected nations. She highlights the importance of engaging climate finance providers, multilateral development banks, humanitarian organizations, and peacebuilding actors in finding solutions. A global pact that includes actionable solutions such as streamlined application procedures, adjusted eligibility criteria for conflict-affected actors, and increased flexibility in project locations could drive progress in climate adaptation efforts.
“It won’t be all different at COP28, but we do really want to see a very big step forward at COP28. And this could, for example — and that would be my dream outcome — be in the form of some sort of global pact that all of these actors would sign up to that doesn’t include just principles that we all agree on, but that also would include at least a couple of solutions to these issues,” De Jong said.
“Our proposal is mainly the global pact that I mentioned. So this would focus more, I guess, on changes in the policy spectrum. But it could, for example, also include like a regional capacity-strengthening facility that would help governments apply and develop strong adaptation projects that would then basically build a pipeline of adaptation projects which would help them in the long run, so it wouldn’t necessarily include a fund,” De Jong said.
With the presidency of COP28, the UAE aims to create a platform that brings together various actors to collectively explore solutions. De Jong stresses the need to leverage existing momentum for change, emphasizing that COP28 is a stepping stone toward addressing these complex issues comprehensively.