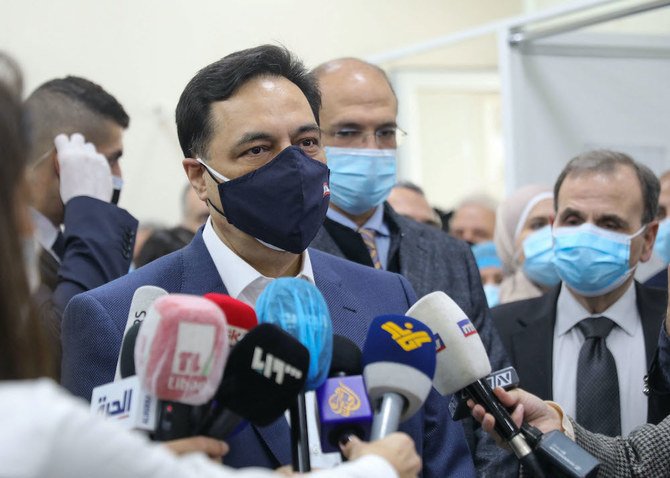
BEIRUT: Lebanon is “in the heart of great danger,” and needs friendly countries to save it, the caretaker prime minister, Hassan Diab, said on Wednesday.
“Either you save it now before it’s too late or else no regrets will help,” Diab said in a televised address. Lebanon is in the throes of a deep financial crisis that is posing the biggest threat to its stability since the 1975-1990 civil war.
Diab has been steering the government in a caretaker role since his cabinet resigned in the aftermath of the Aug. 4 Beirut port blast, which devastated large swathes of the capital, killed hundreds of people and injured thousands.
Prime Minister-desginate Saad Al-Hariri has been at loggerheads with President Michel Aoun over naming cabinet ministers for ten months as the country hurtles toward economic collapse. A new government capable of introducing reforms is necessary to unlock much needed foreign aid.
“I call on political powers to present concessions, and those will be small no matter how big they may seem, because that will alleviate the suffering of the Lebanese and stop this frightening path,” Diab said.
Under a sectarian power-sharing system, Lebanon’s president must be a Maronite Christian and the prime minister a Sunni Muslim. Aoun, a Christian, is an ally of the Iran-backed Shiite movement Hezbollah, listed as a terrorist group by the United States.
Hariri, a veteran Sunni politician, has said the only way out of Lebanon’s crisis is through mending relations with its Arab neighbors.
This comes as Lebanon’s president and prime minister-designate traded barbs Wednesday, accusing one another of obstruction, negligence and insolence in a war or words that has for months obstructed the formation of a new government as the country sinks deeper into economic and financial crisis.
The power struggle between Hariri, on one side and Aoun and his son-in-law Gebran Bassil on the other, has worsened despite warnings from world leaders and economic experts of the dire economic conditions tiny Lebanon is facing. The World Bank on Tuesday said Lebanon’s crisis is one of the worst the world has seen in the past 150 years.
In a reflection of the growing turmoil, scores of Lebanese lined up in front of ATM machines late on Wednesday, after a top court suspended a Central Bank decree that allowed them to withdraw from dollar deposits at a rate two and a half times better than the fixed exchange rate.
The Lebanese pound, pegged to the dollar for 30 years at 1,507, has been in a free fall since late 2019. It is now trading at nearly 13,000 to the dollar at the black market.
Hariri blames the president for the months-long delay, accusing him of insisting on having veto power in the upcoming government.
Aoun, an ally of the powerful militant Hezbollah group, has said that Hariri did not shoulder his responsibilities in forming a government they both can agree on. There is no legal avenue for the president to fire the prime minister-designate, who is chosen to the post by a majority of lawmakers.
The rift has paralyzed the cash-strapped country, delaying urgently needed reforms. The economic crisis, which erupted in 2019, has been compounded by the impact of the coronavirus pandemic on Lebanon and the massive blast at Beirut’s port last year that killed over 200 people and defaced a big section of the capital.
The crisis has driven more than half of the population into poverty, caused the local currency to lose more than 85% of its value, and prompted banks to lock deposits through informal capital controls, eroding trust in a once-thriving banking sector.
The country’s highest administrative court on Tuesday ordered the temporary suspension of a Central Bank circular that gave depositors a chance to withdraw at a rate better than the pegged rate.
The Central Bank announced late Wednesday it was accepting the decision, prompting the queues outside ATMS. One man said he went from one ATM to another to withdraw as much as he could. Another complained that people’s savings are at the mercy of corrupt politicians.
“This is not resilience. We got used to being humiliated and controlled this much by the politicians,” said Mustafa Taoush, a 23-year-old who failed to withdraw more than a weekly limit imposed on withdrawals.
A statement from Aoun’s office on Wednesday accused Hariri of trying to usurp presidential powers, and coming up with “delusional propositions and insolent expressions.”
“The prime minister-designate ’s continuous evading of responsibilities … constitutes a persistent violation of the constitution and national accord,” it added.
Hariri and his political group, the Future party, responded by saying the presidency is “hostage to the personal ambitions” of Bassil, Aoun’s son-in-law, alluding to his alleged presidential aspirations.
High-level mediation efforts from France and local powerful players, including the parliament speaker and the head of the Maronite Church, have faded without a breakthrough in the face of intransigence from the rival parties in Lebanon.
Amid the Aoun-Hariri barbs, caretaker Prime Minister Hassan Diab warned that a collapse of Lebanon could have consequences beyond its borders, hinting at a possible massive exodus of refugees.
Diab, whose Cabinet resigned days after the port explosion, appealed on politicians to make concessions so that a new Cabinet could be formed — one that could resume talks with the International Monetary Fund on how to get out of the crisis.
“The collapse, if it happens, God forbid, will have very grave consequences not only for the Lebanese or those living here but also on friendly countries from the land and sea,” Diab said. “No one will be able to control what waves the sea bring.”
(With Reuters and AP)